Liquid Level Sensors
Liquid level sensing is very important in many applications in which monitoring of the liquid's volume is required. This is particularly useful for flammable hydrocarbons or fuels and of chemicals in industrial and processing plants. Over the years, a wide range of liquid level sensing techniques based on mechanical, electrical, and optical methods has been reported. Electrical liquid level sensors are widely employed, but their application is limited if the liquid to be monitored is conductive or corrosive or if the environment is potentially explosive. Optical fibers offer several advantages as compared to other technologies, and they have been the subject of intense research for several years. Some of the key advantages include low power consumption, ability to withstand corrosive environments, immunity from electromagnetic interference, large distance between signal generation/detection, and high sensitivity. Therefore, liquid level sensing of flammable fluids or explosive environments are well suited applications for optical fiber sensors, because they do not require electrical signals.
In general, for liquid level measurement we have two types of level sensor: continuous measurement and discrete or point measurement. Continuous monitoring of the liquid level typically employs evanescent wave interaction in order to monitor the liquid level in real time. Discrete sensors are designed to detect the presence of liquids at a particular point by using exposed fiber gratings and special fiber tips, which rely on intensity variations as the liquid level makes contact with the sensing region.
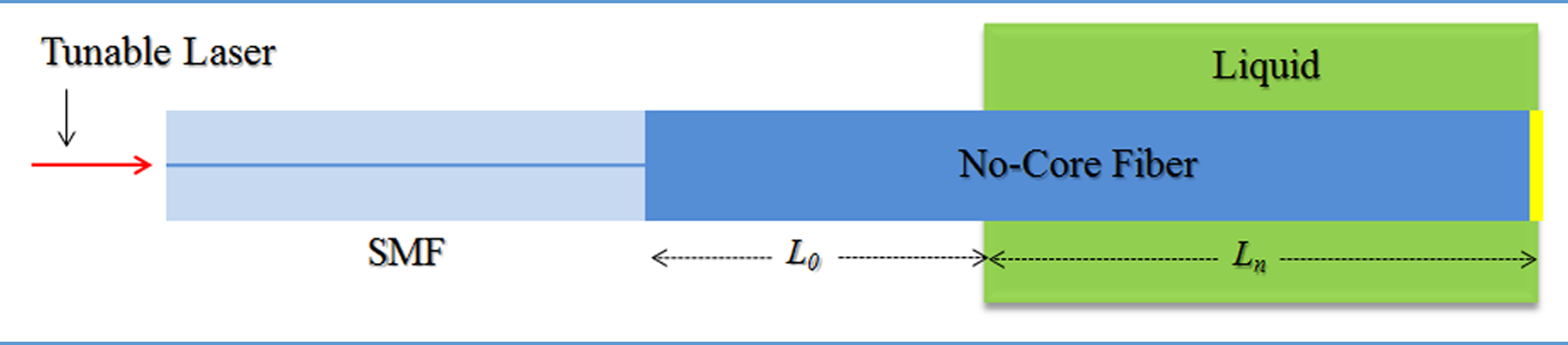
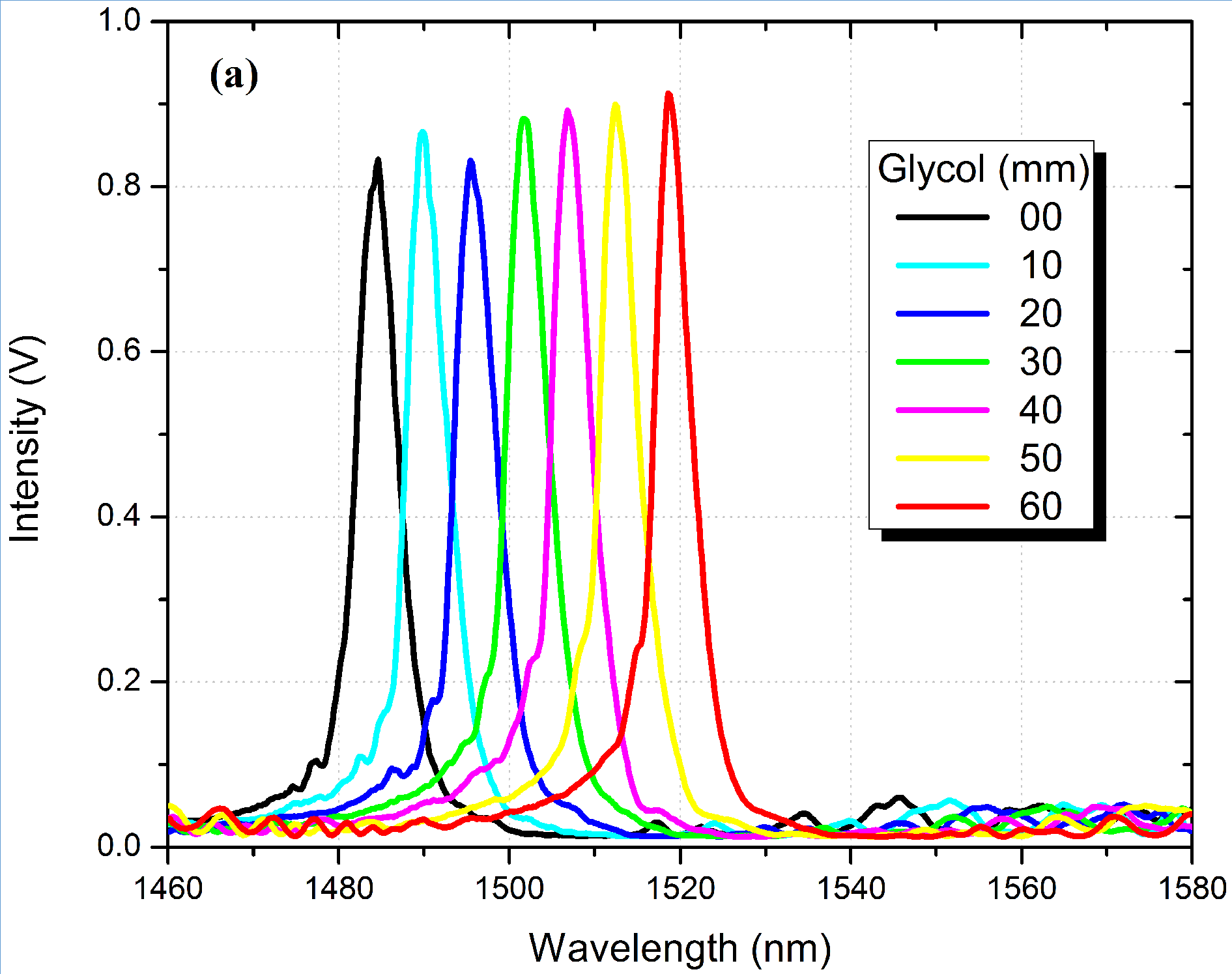
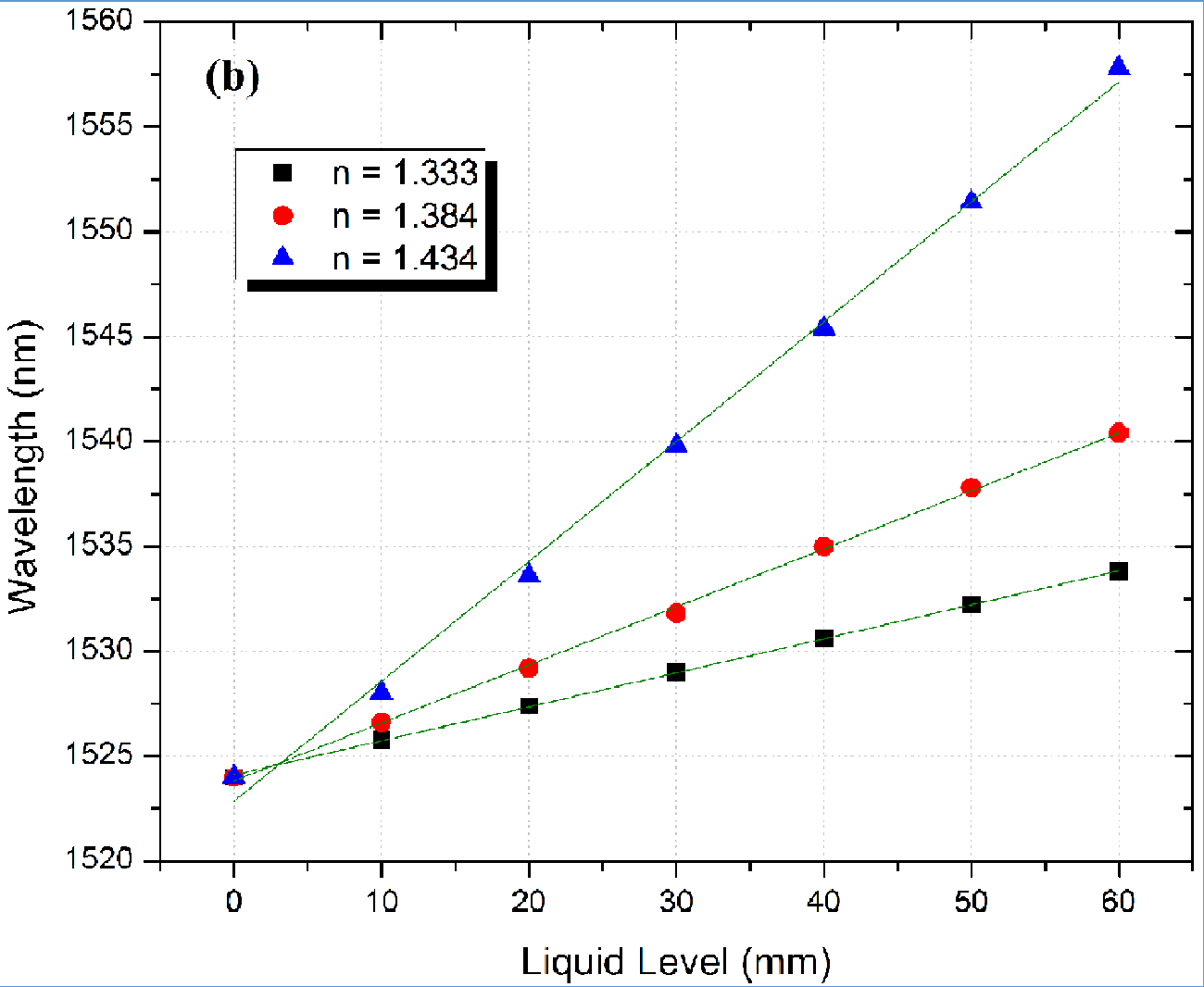
Continuous liquid level sensor using a No-Core multimode fiber as the sensing element.
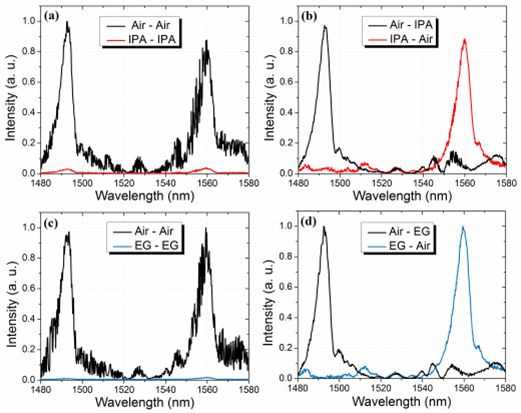
Discrete liquid level sensor using a 105/125 multimode fiber as the sensing element.
Related Publications:
- J. E. Antonio-Lopez, D. A. May-Arrioja, and P. LiKamWa, "Fiber Optic Liquid Level Sensor", Photonics Technology Letters, vol. 23, no. 23, pp. 1826-1828, December (2011).
- J. E. Antonio-Lopez, J. J. Sanchez-Mondragon, P. LiKamWa, and D. A. May-Arrioja, "Fiber Optics Sensor for Liquid Level Measurement", Optics Letters, vol. 36, no. 17, pp. 3425-3427, Septiembre 2011.
