Photonic Switches
As a result of the continuous growth of telecom-based applications, such as internet and video on demand, the requirements for information transmission capacity have increased dramatically over the past two decades. The net result is the need for the deployment of high-capacity networks that can handle tremendous amount of information. A challenge for these networks is to offer high-speed routing capabilities that can handle such massive flows of information. Current technologies are reaching an upper limit as higher speeds are required. A more convenient way is to take advantage of the recent technological progress in advanced integrated photonic devices. Among the many photonic devices, photonic switches are becoming key components because they can perform a variety of applications, particularly in signal routing and time division signal processing. In these applications, the optical transparency of photonic switch modules offers simplified and higher capacity system operation, by allowing networking function to be lowered to the optical layer. One of the major advantages of photonic switches is that they avoid the need for optical-electronic and electronic-optical (o-e-o) conversions. Such conversions not only limit the versatility and transparency of the system, but can also amount to signal deterioration and errors introductions. In fact, the elimination of such o-e-o conversions will result in a major decrease in the overall system cost, since the equipment associated with these conversions represents the main cost associated in today's networks.
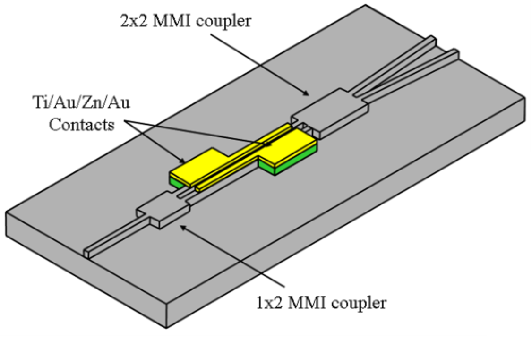
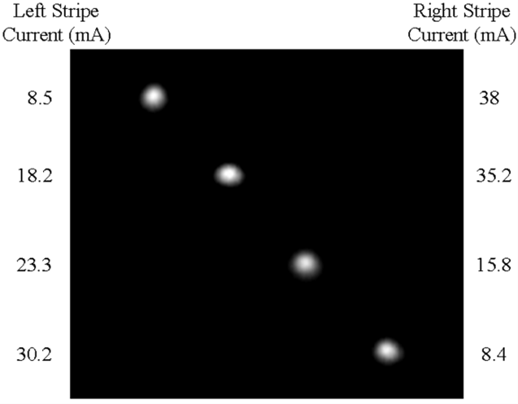
Integrated 1x4 photonic switch based on beam steering technology.
Related Publications:
- D. A. May-Arrioja and P. LiKamWa, "Reconfigurable 1x4 InP-Based Optical Switch", Microelectronics Journal, vol.39, pp. 644-647, 2008.
- D. A. May-Arrioja, N. Bickel, and P. LiKamWa, "Robust 2x2 Multimode Interference Optical Switch", Optical and Quantum Electronics, vol. 38, no. 7, pp. 557-566, May 2006.
